Hello my friends! Today I would like to talk about the Linux world once again. In a previous post we saw how to set up a LAMP server in Linux Ubuntu. Basically the installation of LAMP provides a default website, or a “virtualhost” as they are called in Apache, with a default web page. This is the default page we are talking about:
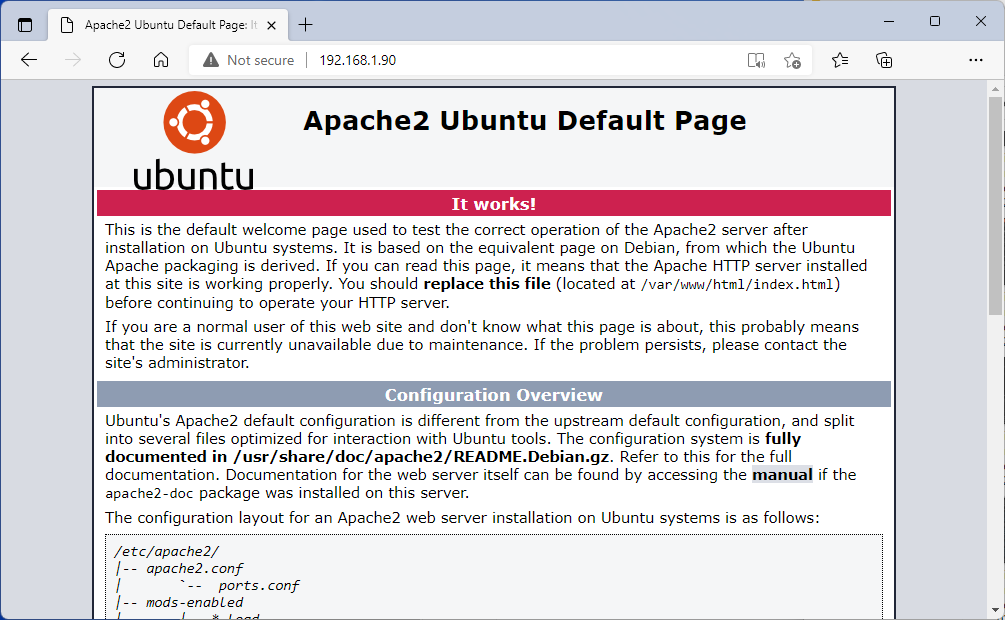
If you are planning to have a single website running in your server, you can simply work with this default virtualhost. But, if you need to host multiple websites in your Apache installation, you have to add a new virtual host for each site. We will see how in the next paragraphs.
The Apache configuration file
To create a new virtualhost in our Apache installation we have to modify the Apache configuration file, which is usually located in /etc/apache2/apache2.conf. But pay attention…
In some installations, and this is true also for Linux Ubuntu, the apache2.conf doesn’t contains the complete Apache configuration. Some configuration pieces are stored in separate files and this applies to virtualhosts. So to create a new virtualhost, we have to create a new file in the correct location.
Add a new virtualhost
You can find virtualhost configuration files in the directory /etc/apache2/sites-available.
If you list the content of the directory with the command
ls -lyou will see the following files:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1332 Sep 30 2020 000-default.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6338 Sep 30 2020 default-ssl.confThis is what they contain:
- 000-default.conf: is the configuration of the virtualhost that is listening on http port 80
- default-ssl.conf: is the configuration of the virtualhost that is listening on ssl port 443
We want to create a new virtualhost that responds on port 80 to a certain URL, for example “www.mytestsite.com”.
The website name is random, you can use whatever name you want and, don’t worry, you don’t have to buy a domain to see it working because we will see a little trick to make it work with our local virtual machine.
Let’s start by making a copy of the first file, so run the following command:
cp /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/mytestsite.com.conf We need to modify the file to contain the content below. Since we copied it from the default file, a part of it should already be ready.
<VirtualHost *:80>
# The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that
# the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
# redirection URLs. In the context of virtual hosts, the ServerName
# specifies what hostname must appear in the request's Host: header to
# match this virtual host. For the default virtual host (this file) this
# value is not decisive as it is used as a last resort host regardless.
# However, you must set it for any further virtual host explicitly.
ServerName mytestsite.com
ServerAlias www.mytestsite.com
ServerAdmin webmaster@mytestsite.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/mytestsite.com/public_html
<Directory /var/www/mytestsite.com/public_html>
Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
# Available loglevels: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
# error, crit, alert, emerg.
# It is also possible to configure the loglevel for particular
# modules, e.g.
#LogLevel info ssl:warn
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/mytestsite_error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/mytestsite_access.log combined
# For most configuration files from conf-available/, which are
# enabled or disabled at a global level, it is possible to
# include a line for only one particular virtual host. For example the
# following line enables the CGI configuration for this host only
# after it has been globally disabled with "a2disconf".
#Include conf-available/serve-cgi-bin.conf
</VirtualHost>Now we are going to create the directory that will contain our new website. Note that this must match the directory specified in the option “DocumentRoot” and in the tag “Directory” of the configuration file.
sudo mkdir /var/www/mytestsite.com
sudo mkdir /var/www/mytestsite.com/public_htmlIn the folder “/var/www/mytestsite.com/public_html” create a file “index.html” with this simple content:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>This my test site!</title>
<body>
<h1>This is my test site!</h1>
</body>
</html>Execute the following command to “register” our new virtualhost. Note that parameter “mytestsite.com” must match the file name you created in /etc/apache2/sites-available, but without the suffix “.conf”.
sudo a2ensite mytestsite.comAnd then restart the Apache service:
sudo service apache2 restartTo make the website reachable from our Windows host operating system, we have to add the following line to the Windows host file, which is located under “C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc”:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
# space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhost
192.168.1.90 www.mytestsite.com # this the new line
The line added is the last one. Remember that in my case 192.168.1.90 is the address of my VirtualBox Host-Only Network adapter, your address may be different.
That’s it, now if you type the address www.mytestsite.com in your Windows host browser, you should see test page we created above:
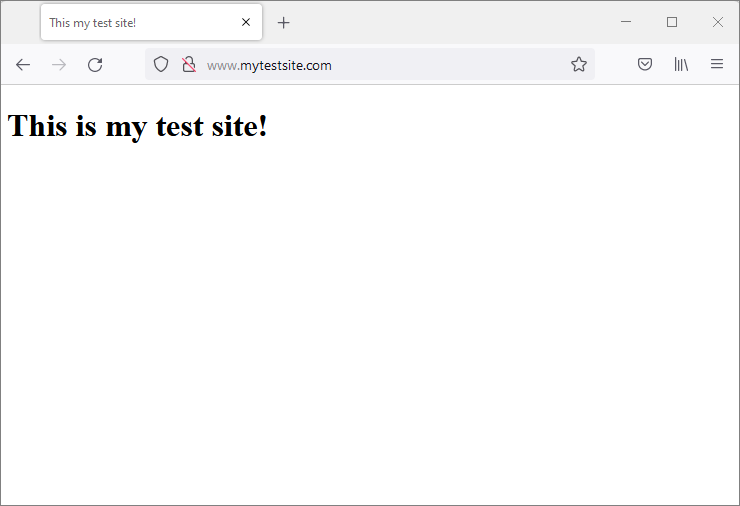
For the moment we can close here … I hope this post was useful. Let me know your comments!